How MongoDB Works
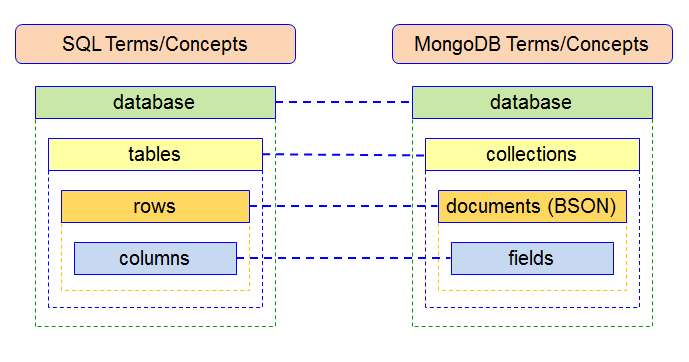
MongoDB is a document-oriented, NoSQL database that stores data in a JSON-like format, which is often referred to as BSON (Binary JSON). Unlike traditional relational databases, MongoDB does not use a fixed schema or table structure, but rather stores data in flexible and dynamic documents.
Here's how MongoDB works based on the following points:
Database :
In MongoDB, a database is a container for collections. It is where all the data is stored. You can think of a database as a namespace for collections. You can create as many databases as you need, and each database can have one or more collections.
Collections :
A collection in MongoDB is a group of related documents. It is similar to a table in a relational database, but without a fixed schema. You can add or remove fields to a collection at any time, without affecting other documents in the collection. A collection can have one or more indexes, which can be used to optimize query performance.
Documents :
A document in MongoDB is a JSON-like data structure that represents a single instance of data. It is similar to a row in a relational database, but with a more flexible and dynamic structure. A document can contain any number of fields, which can be of different data types, and can have nested structures.
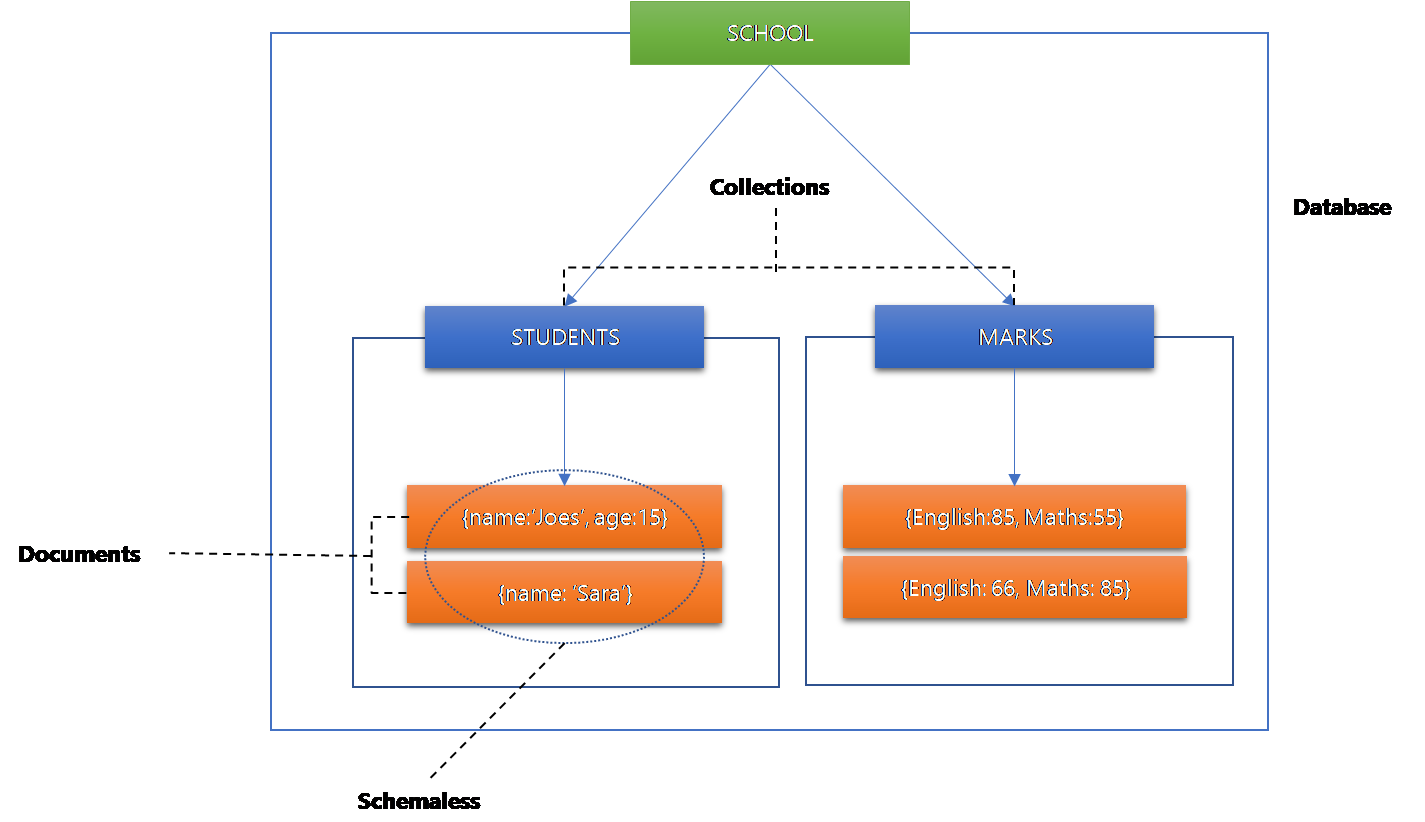
Documents in a collection do not have to follow a fixed schema, allowing for more flexibility in data modeling. For example, one document in a collection could have additional fields compared to other documents. This schemaless approach is one of the key features of MongoDB.
To summarize, MongoDB stores data in a JSON-like format, with a flexible and dynamic structure, without a fixed schema. Data is organized into databases, which contain collections of related documents. This document-oriented approach offers greater flexibility and scalability than traditional relational databases, making it popular for web and mobile applications that require high performance and scalability.
| Description | MySQL | MongoDB |
|---|---|---|
| Data Storage | Tables | Collections |
| Data Record | Row | Document |
| Field | Column | Field |
| Index | Index | Index |
| Primary Key | Primary Key | Primary Key (automatically created for the _id field) |
| Query Language | Structured Query Language (SQL) | MongoDB Query Language (MQL) |
| Joining Tables | JOIN clause | Embedded documents or manual references |
| Transactions | ACID-compliant transactions | Multi-document transactions (in recent versions) |
| Replication | Master-slave replication | Replica sets |
| Sharding | Partitioning based on a sharding key | Sharding based on a sharding key or hashed shard key |
| Data Modeling | ER modeling | No fixed schema, document-oriented data modeling |
| Use Cases | Traditional data-driven applications | Web applications, real-time analytics, and high-volume transactional systems |
MongoDB Tutorial
Learn All in Tamil © Designed & Developed By Tutor Joes | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions