Accounting Equation
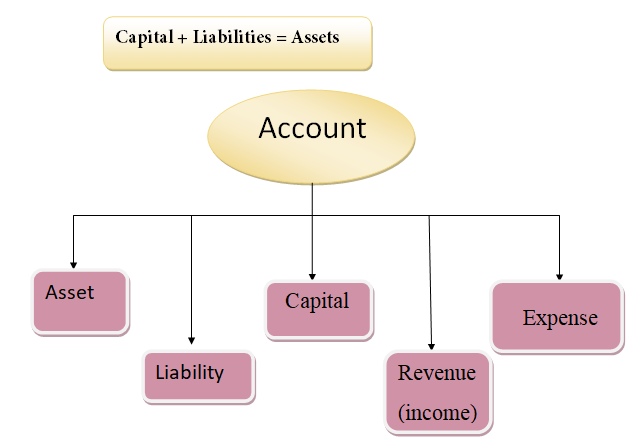
Asset account
Any physical thing or right owned that has a monetary value is called asset. for example, Land and Buildings account, Plant and Machinery account.
Liability account
Financial obligations of the enterprise towards outsiders are shown under separate heads as liabilities; for example, creditors account, expenses outstanding account.
Capital account
Financial obligations of a business enterprise towards its owners are grouped under this category; for example, capital contributed by owner.
Revenue account
Accounts relating to revenues of an enterprise are grouped under this category, for example; revenues from sale of goods, rent received.
Expense account
Expenses incurred and losses suffered for earning revenue are grouped under this category; for example, purchase of goods, salaries paid.
- In every business transaction, there are two aspects.
- The two aspects involved are the benefit or value receiving aspect and benefit or value giving aspect.
- These two aspects involve minimum two accounts; at least one debit and at least one credit.
- For every debit, there is a corresponding and equivalent credit. If one account is debited the other account must be credited.
Advantages of double entry system
Following are the advantages of double entry system:
- Accuracy
- Ascertainment of business results
- Comparative study
- Common acceptance
Transaction
Transaction can be classified into cash transaction, bank transaction and credit transaction.
Cash transaction
When immediate cash is involved in a transaction, it is called cash transaction. For example, goods are sold for cash ` 5,000. In this case, cash ` 5,000 comes into the business and goods worth ` 5,000 go out of the business.
Bank transaction
In a transaction, if bank is involved, it is a bank transaction.
- Cash deposited into the bank
- Income of the business directly received by the bank
- Receipts through Cash Deposit Machine (CDM)
- Payment made by the customers of the business through debit card, credit card, net banking, National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT), Real Time Gross Settlement (RTGS), etc.
- Cash withdrawn from the bank
- Bank charges levied by the bank
- Payments made by the bank as per standing instructions
- Payments made by cheque
- Payments made by the business through debit card, net banking, NEFT and RTGS
Credit transaction
When settlement is not made by cash or through bank immediately in a transaction, it is called credit transaction. For example, purchase of goods on credit for `3,000. In this case, goods worth `3,000 come into the business and a liability of creditors worth ` 3,000 arises.
Gold and rules
| Type of account | debit | credit |
|---|---|---|
| personal | The receiver | The giver |
| Real | What comes in | What goes out |
| nominal | All Expenses and losses | All income and gains |
Classification of accounts:
Personal account
These are account relating to individuals, a group of individuals, firms and institutions.
-
Ex.
- Mr. karthik (individual account)
- Canara Bank (institution’s account)
- Gopalam (partnership firm)
Real account:
These are account relating to the property or asset and cash belonging to a business concern.
-
Ex.
- Land and building (asset)
- Cash-in hand(asset)
- Purchases, Goodwill, etc.
Nominal account
These are accounts relating to the incomes, expenses, losses and gains of a business concern.
-
Ex.
- Salary accounts
- Discount allowed
- Discount received, etc.
Basic of Accounts
Learn All in Tamil © Designed & Developed By Tutor Joes | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions